Introduction
Receding gums, or gingival recession, is a common dental issue where the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away, exposing more of the tooth or its root. This condition can lead to sensitivity, increased risk of decay, and aesthetic concerns. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, prevention strategies, and treatment options for receding gums.
Overview
- Understanding Receding Gums
- Causes of Receding Gums
- Symptoms of Receding Gums
- Prevention Strategies
- Home Remedies for Receding Gums
- Professional Treatments for Receding Gums
- Lifestyle Changes to Support Gum Health
- Conclusion
Understanding Receding Gums

What Are Receding Gums?
Receding gums occur when the gum tissue that surrounds the teeth pulls back or wears away, exposing more of the tooth or its root. This can lead to pockets forming between the teeth and gums, making it easier for disease-causing bacteria to build up.
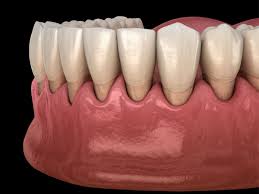
Why Are Receding Gums a Concern?
Receding gums can be a significant concern for several reasons:
- Aesthetic Issues: Exposed roots can affect the appearance of your smile.
- Sensitivity: Exposed roots can lead to increased sensitivity to hot, cold, and sweet foods.
- Decay: Exposed roots are more susceptible to decay and other dental issues.
- Bone Loss: If left untreated, receding gums can lead to bone loss around the teeth, eventually leading to tooth loss.
Causes of Receding Gums
Understanding the causes of receding gums is crucial for prevention and treatment. Here are some common causes:
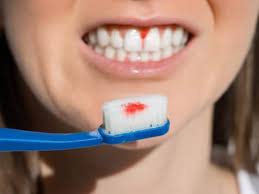
Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, which can cause gum disease and lead to receding gums.

Aggressive Brushing
Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can damage the gum tissue and cause it to recede.
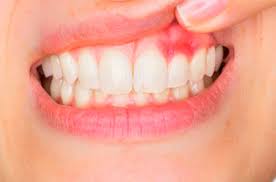
Gum Disease
Periodontal diseases, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, are major causes of gum recession. These conditions result from bacterial infections that damage the gum tissue and supporting bone.
Genetic Factors
Some people are more prone to gum disease and receding gums due to genetic factors.

Hormonal Changes
Fluctuations in hormones, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can make gums more sensitive and susceptible to recession.

Tobacco Use
Smoking or using other tobacco products can damage your gums and cause them to recede.
Misaligned Teeth or Bite
Misaligned teeth or an improper bite can place excessive force on the gums and bone, leading to gum recession.
Teeth Grinding and Clenching
Bruxism, or teeth grinding and clenching, can exert too much force on the teeth and gums, causing them to recede.
Body Piercings
Oral piercings, such as lip or tongue piercings, can rub against the gums and cause irritation, leading to recession.

Symptoms of Receding Gums
Recognizing the symptoms of receding gums is essential for early intervention and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Tooth Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks.
- Visible Roots: Noticeable exposure of the tooth roots.
- Longer Teeth: Teeth appearing longer than usual due to gum loss.
- Gum Inflammation: Red, swollen, or bleeding gums.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth.
- Loose Teeth: Teeth that feel loose or unstable.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing receding gums involves maintaining good oral hygiene and adopting healthy habits. Here are some effective strategies:
Proper Brushing Techniques
- Use a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush: Soft bristles are gentle on the gums.
- Brush Gently: Avoid aggressive brushing; use gentle, circular motions.
- Brush Twice Daily: Brush your teeth at least twice a day for two minutes each time.
Regular Flossing
- Daily Flossing: Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth.
- Gentle Flossing: Be gentle when flossing to avoid damaging the gums.
Use Mouthwash
- Antibacterial Mouthwash: Use an antibacterial mouthwash to help reduce plaque and prevent gum disease.
Regular Dental Check-Ups
- Biannual Visits: Visit your dentist at least twice a year for professional cleanings and check-ups.
- Early Detection: Regular dental visits help detect and treat gum recession early.
Healthy Diet
- Balanced Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support gum health.
- Limit Sugary Foods: Reduce the intake of sugary and acidic foods and drinks that can contribute to plaque buildup.

Avoid Tobacco
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, seek help to quit. Avoid using other tobacco products as well.
Manage Stress
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or exercise, to help prevent teeth grinding and clenching.

Home Remedies for Receding Gums
While professional treatment is essential for advanced cases, several home remedies can help manage mild gum recession and support overall gum health:

Oil Pulling
- Coconut or Sesame Oil: Swish a tablespoon of oil in your mouth for 15-20 minutes daily to reduce plaque and bacteria.

Saltwater Rinse
- Saltwater Solution: Rinse your mouth with a mixture of salt and warm water to reduce inflammation and bacteria.
Aloe Vera
- Aloe Vera Gel: Apply aloe vera gel directly to the gums to soothe inflammation and promote healing.

Green Tea
- Green Tea Consumption: Drink green tea regularly to take advantage of its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Eucalyptus Oil
- Diluted Eucalyptus Oil: Use diluted eucalyptus oil as a mouth rinse to reduce bacteria and inflammation.

Omega-3 Supplements
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Take omega-3 supplements to help reduce inflammation and promote gum health.
Professional Treatments for Receding Gums
When home remedies and preventive measures are not enough, professional dental treatments can help manage and reverse gum recession:

Scaling and Root Planing
- Deep Cleaning: This procedure involves a deep cleaning of the gums to remove plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line.
- Root Smoothing: Smoothing the roots of the teeth helps the gums reattach to the teeth.
Gum Grafting
- Tissue Grafting: A gum graft involves taking tissue from another part of the mouth (or using donor tissue) and attaching it to the receded gum area.
- Healing and Integration: The grafted tissue integrates with the existing gum tissue, covering exposed roots and reducing sensitivity.
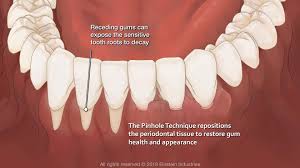
Pinhole Surgical Technique
- Minimally Invasive: This technique involves making a small hole in the gum and using special instruments to loosen and reposition the gum tissue.
- Quick Recovery: This procedure offers a quicker recovery time compared to traditional gum grafting.
Regenerative Procedures
- Guided Tissue Regeneration: This procedure involves placing a membrane between the gum and bone to encourage new tissue growth.
- Bone Grafts: Bone grafts may be used in conjunction with other procedures to support new bone and tissue growth.
Laser Therapy
- Laser Treatment: Lasers can be used to remove infected gum tissue and promote healing, reducing the need for invasive surgery.
Orthodontics
- Correcting Misalignment: Braces or other orthodontic treatments can help correct misaligned teeth or bites, reducing the risk of gum recession.

Lifestyle Changes to Support Gum Health
In addition to specific treatments and preventive measures, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly support gum health and prevent recession:

Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
- Consistent Routine: Brush and floss regularly, and use mouthwash as needed.
- Choose the Right Products: Use toothpaste and mouthwash designed for gum health.

Healthy Diet
- Nutrient-Rich Foods: Consume a diet rich in vitamins C and D, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and help maintain saliva production.

Stress Management
- Relaxation Techniques: Practice yoga, meditation, or other relaxation techniques to manage stress and reduce the risk of teeth grinding.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to promote overall health and reduce stress.

Avoid Harmful Habits
- Quit Smoking: Seek help to quit smoking and avoid other tobacco products.
- Limit Alcohol: Reduce alcohol consumption, as excessive alcohol can contribute to gum disease.

Regular Dental Visits
- Routine Check-Ups: Schedule regular dental visits for cleanings and check-ups.
- Professional Advice: Consult your dentist for personalized advice on maintaining gum health.
Conclusion
Receding gums can be a concerning dental issue, but with proper care, prevention, and treatment, it is possible to manage and even reverse gum recession. By understanding the causes and symptoms, adopting effective prevention strategies, and seeking professional treatment when necessary, you can maintain healthy gums and protect your smile. Remember to practice good oral hygiene, make healthy lifestyle choices, and visit your dentist regularly to keep your gums in top condition.
Taking proactive steps today can lead to a healthier, more confident smile tomorrow. Whether you are experiencing mild gum recession or seeking ways to prevent it, this comprehensive guide provides the information you need to take charge of your gum health.

